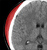
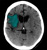
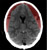
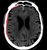
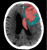
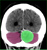
Extradural haematoma (EDH) with contrecoup injury
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
Extradural haematoma (EDH) with contrecoup injury
- A lens-shaped collection of dense (acute) blood is the classic appearance of an extradural haematoma (EDH)
- EDH formation commonly results from injury to the middle meningeal artery
- Post-traumatic intracranial haemorrhage at the site of impact can be referred to as a 'coup' injury
- A coup injury may be accompanied by a 'contrecoup' injury - located on the opposite side of the brain from the site of impact
- Contrecoup injuries are caused by acceleration-deceleration forces at the time of injury
Clinical information
- Fall from height with direct trauma to the left side of the head