Elbow - Supracondylar fracture - Lateral
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
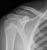
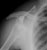
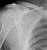
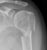
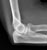
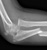
Elbow - Supracondylar fracture - Lateral
- This is the commonest elbow fracture in children
- A joint effusion raises the anterior and posterior fat pads, indicating intra-capsular injury
- Less than one third of the capitulum of the humerus lies in front of the anterior humeral line
- The distal fracture fragment is pulled posteriorly by the triceps muscle
- These signs indicate a fracture even if a fracture line is not visible
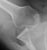
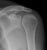
Elbow - Supracondylar fracture - AP
Hover on/off image to show/hide findings
Tap on/off image to show/hide findings
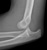
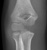
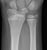
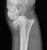
Elbow - Supracondylar fracture - AP
- The fracture line is also seen clearly on the AP image in this case